 «ТАСДИҚЛАЙМАН»
«ТАСДИҚЛАЙМАН»
Ўкув ишлари бўйича биринчи проректор
_______________________________
“_____”________________2016 йил
ЧЕТ ТИЛЛАР КАФЕДРАСИ
ЧЕТ ТИЛИ ФАНИДАН
МАХСУС СИРТҚИ БАКАЛАВР ЙЎНАЛИШИ ТАЛАБАЛАРИ УЧУН
O’QUV USLUBIY MAJMUA
Мазкур ўқув-услубий мажмуа Олий ва ўрта махсус таълим вазирлигининг 2013 йил 28 августдаги 319-сонли буйруғи билан тасдиқланган ўқув режа ва дастур асосида 5350200-Тelevizion texnologiyalari(“ Audiovizual texnologiyalari”,”Теlestudiya tizimlari va dasturlari”) таълим йуналишлари учун ишлаб чикилган
Тузувчилар: М.Т. Шахакимова
В.Х. Газиева
Такризчилар: А.Т. Ирискулов
«ЧЕТ ТИЛЛАР» кафедрасининг 30.08.2016 йилдаги йиғилишида
мухокама килинган (1-сонли баённома)
Кафедра мудири В. Х. Газиева
« ЧЕТ ТИЛЛАР » факультетининг 31.08.2016 йилдаги кенгашида тасдикланган (1-сонли баённома)
Факультет кенгаши раиси Ш.Ш.Тураев
МУНДАРИЖА
1.СИЛАБУС........................................................................................................
2. ФАННИ ЎҚИТИШДА ФОЙДАЛАНИЛАДИГАН ИНТЕРФАОЛ ТАЪЛИМ МЕТОДЛАРИ ...................................................................................
3 АМАЛИЙ МАШҒУЛОТЛАР МАТЕРИАЛЛАРИ ........................................
4. МУСТАҚИЛ ТАЪЛИМ МАВЗУЛАРИ ........................................................
5. ГЛОССАРИЙ .................................................................................................
6. АДАБИЁТЛАР РЎЙХАТИ.............................................................................
I. SILLABUS
2016/2017 O’QUV YILI
Fanning qisqacha tavsifi
|
OTM nomi va manziii |
Toshkent axborot texnologiyalari universiteti |
Amir Temur 108, Toshkent |
|
|
Fakultet va kafedra |
AKT sohasida Iqtisodiyot va Menejment |
Chet tili |
|
|
Ta'lim vo’nalishi |
5350200-Тelevizion texnologiyalari(“ Audiovizual texnologiyalari”,”Теlestudiya tizimlari va dasturlari”)
|
||
|
Fanning professor - o'qituvchilari haqida ma’lumot
|
Amaliyot: |
e-mail: Телефон: |
gaziyeva@inbox.ru +998712386467 |
|
Fanning jadvali va auditoriya №.
|
142 c |
Fanni o’qitish muddati: |
2016-17 o’quv yili |
|
Fanga ajratilgan soatlar |
Auditoriya mashg’ulotlari barcha bosqichloar uchun (1/2/3 kurs) yaarim o’qquuv yilliga |
Mustaqil ta’lim: 1 – 2 kurs uchun 80 soat 3 kurs uchun 60 soat
|
|
|
Amaliyot : 1 – 2 kurs uchun 16soat 3 kurs uchun 12 soat 3 kurs uuchun 54 |
|||
Fanning mazmuni
Fanning dolzarbligi va mazmuni
Vazirlar Mahkamasining “Chet tillar bo'yicha ta'limning barcha bosqichlari bitiruvchilarining tayyorgarlik darajasiga qo'yiladigan talablar”ga ko'ra oliy ta'lim muassasalarining ixtisosligi chet tili bo'lmagan fakultetlari bakalavriat bosqichi bitiruvchilari to'rt yillik tahsillari nihoyasida o'rgangan chet tili bo'yicha B2 darajani egallashlari lozim.
Ushbu dastur “Chet tili” fanini ikki bosqichga bo'lingan holda o'qitishni nazarda tutadi:
- umumiy bosqich (umumiy chet tili o'rganiladi).
- kasbga yo'naltirilgan bosqich (chet tili maxsus maqsadlarda o'rgatiladi).
Har bir kurs uchun alohida o'quv soatlari ajratilgan. Kurslar bir-biridan mavzusi, leksik tizimi, o'quv matnlari, nutq faoliyatlari xususiyati va mavqeiga qarab malakalarni rivojlantirish bo'yicha farqlansada, o'quv jarayoni uchun umumiy bo'lgan grammatik mavzular, o'xshash sintaktik hodisalar, nutq ko'nikma va malakalarini egallashda o'zaro uzviy bog’liq va uzluksiz holda o'rgatiladi. Chet tilini o'rgatish ixtisoslik xususiyatlaridan kelib chiqib, “Chet tili maxsus maqsadlar uchun” tamoyillariga va kommunikativ, integrativ kompetentlik yondashuvlariga asoslanadi.
Fanning asosiy vazifalari talabalarga chet tilida erkin mulloqot qilish bilan bir qatorda tehnik termin va atamalarni chet tillida ifodalay olishni va qo’llash ko’nikmalarini hosil qilishdan iboratdir.
FANNI O'QITISH SOATLARI TAQSIMOTI
|
Amaliy mashg’ulotlar |
I |
II |
III |
IV |
V |
YI |
|
Amaliy mashg’ulot jami |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
6 |
6 |
|
Fan bo'yicha maksimal ball, soat |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
|
Minimal o'zlashtirish ball |
55 |
55 |
55 |
55 |
55 |
55 |
HAFTALAR BO'YICHA FANNI O'QITISH SOATLARI TAQSIMOTI
HAFTALAR BO'YICHA FANNI O'QITISH SOATLARI TAQSIMOTI
I – IIsemestr
|
№ |
Mashg’ulot turi |
jami |
haftalar |
|||
|
1 |
amaliy |
4 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
jami |
8 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
III-IV semester
|
№ |
Mashg’ulot turi |
jami |
haftalar |
|||
|
1 |
amaliy |
4 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
jami |
8 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V-YI semestr
|
№ |
Mashg’ulot turi |
jami |
haftalar |
||
|
1 |
amaliy |
3 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
jami |
6 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
Модул бўйича соатлар тақсимоти
1 семестр
|
№ |
Амалий машғулот мавзулари
|
Тингловчининг ўқув юкламаси, соат |
|||
|
Аудитория ўқув юкламаси жумладан |
|||||
|
Ҳаммаси |
Жами |
Амалий машғулот |
Мустақил таълим |
||
|
An introductory lesson. Giving personal information Starter: Answering the questions. P 6. Listening: Ex: 1, 2, 3 p. 6-7 Speaking: Career Grammar: Modal verbs: should, must, have to. Ex: 4 a), b) p.7 Writing: Write your future plan |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
2. |
Unit 1. Lesson 1. Ubiquity of English Starter: English ubiquity signs p.10 Listening: Social service destinations Ex 1,2,3 p. 10 Reading: Text: “Working language” Ex.7-9 on p. 12 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
3. |
Lesson 2. Information and security Starter: Working with pictures p.18. Speaking: Ideological attack Reading: Special text. |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
Unit1, Lesson4. Online etiquette-netiquette. Starter: discussing the pictures Listening: EX: 1 ,2, 3, p 22. Speaking: Ex5 p-23. |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
Жами |
88 |
8 |
8 |
80 |
2семестр
|
№ |
Амалий машғулот мавзулари
|
Тингловчининг ўқув юкламаси, соат |
|||
|
Аудитория ўқув юкламаси жумладан |
|||||
|
Ҳаммаси |
Жами |
Амалий машғулот |
Мустақил таълим |
||
|
Unit 2. Lesson 5. Learning strategies Starter: starter ex. .1 Reading: Learning Pyramids Exercises 8, 9,10 Listening: Ex: 1, 2, 3 p. 30-31 Speaking: ex4,5. P-31. |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
2. |
Lesson 7. Succeeding in lifelong learning. Starter: Working with pictures and quotes. P. 38 Speaking: group work: making poster about outstanding person Reading: Ibn Sina (Avicenna) p.40-41. |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
3. |
Lesson 8. Social and Personal Responsibility Starter: Social and personal responsibility Listening: song “Man in the Mirror” by M.Jackson Ex.1, p 42. |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
Unit 3 Types of management . Speaking: Service management Reading: Risk management . |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
|
Жами |
88 |
8 |
8 |
80 |
3семестр
|
№ |
Амалий машғулот мавзулари
|
Тингловчининг ўқув юкламаси, соат |
|||
|
Аудитория ўқув юкламаси жумладан |
|||||
|
Ҳаммаси |
Жами |
Амалий машғулот |
Мустақил таълим |
||
|
Unit 1. Global Problems and Solutions Lesson 1. Problem Cause Listening: Ex: 1, 2, 3, 4 p. 6-7 Speaking: EX: 5-7, p. 7-8, Problem Cause Reading: Types of Problems |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
2. |
Unit 1. Lesson 2. Unintended Consequences Listening: EX: 1,2,3,4. P.10-11 T3 P14 Speaking: Discussion of the lecture Special text. |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
3. |
Unit 1. Lesson 3. Solution Starter: Great Minds quotes. P. 14 Listening: EX: 1,2,3,4. P.10-11 T3. P14 Special text. |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
Unit 2. Research perspectives Lesson 4. Motivation and Inspiration Starter: Eliciting s’s answers, p. 20 Listening: EX: 1-4. P. 20-21 Speaking: Ex: 5-6. P 21. How you are best motivated or inspired? |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
|
Жами |
88 |
8 |
8 |
80 |
4семестр
|
№ |
Амалий машғулот мавзулари
|
Тингловчининг ўқув юкламаси, соат |
|||
|
Аудитория ўқув юкламаси жумладан |
|||||
|
Ҳаммаси |
Жами |
Амалий машғулот |
Мустақил таълим |
||
|
Unit 2. Research perspectives Lesson 5. Field of Interest Starter: Working with photo and eliciting s’s answers Listening: EX: 1-3. P. 24-25 Speaking: EX: 4. P. 25 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
2. |
Lesson 6. Conference Participation Starter: Working with pictures. Eliciting answers. Listening: EX: 1-3. P. 28-29 Speaking: EX: 4. P. 29 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
3. |
Lesson 7. Investigating Skills Starter: Working with pictures. P. 34. Listening: EX: 1-4. P. 34 Speaking: EX: 5. P.35 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
Lesson 8. Research Issues. Grammar: Transition words. EX: 6-8. P. 39 Listening: EX: 1-5. P. 38-39 Special text. |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
|
Жами |
88 |
8 |
8 |
80 |
5семестр
|
№ |
Амалий машғулот мавзулари
|
Тингловчининг ўқув юкламаси, соат |
|||
|
Аудитория ўқув юкламаси жумладан |
|||||
|
Ҳаммаси |
Жами |
Амалий машғулот |
Мустақил таълим |
||
|
Unit 1. World’s new vision Lesson 1. Academic fields Starter: Matching headings. P.6 Listening: Ex: 2, 3, p. 7 Speaking: EX: 4,9 p. 7-9 Academic disciplines |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
2. |
Unit 1. Lesson 2. Scientific break throughs Starter: Warming up P.10 Listening: EX: 3. P.11 Reading: EX: 7,8,9.10 P. 12
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
3. |
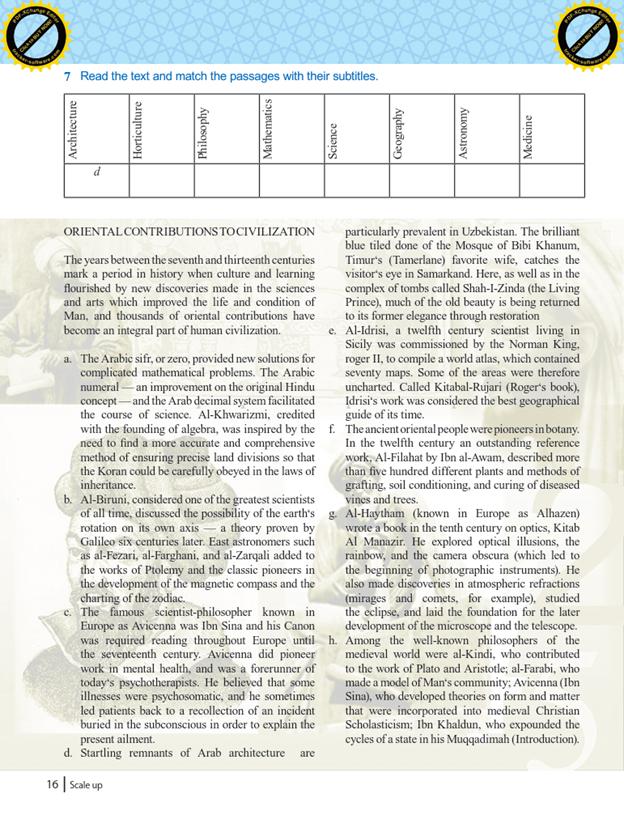
Unit 1. Lesson 3. Oriental contribution Starter: Guessing. P. 14 Listening: EX: 2,3,. P.15 T Speaking: Oriental ancestors EX: 4, p, 15 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
Жами |
|
6 |
6 |
60 |
6семестр
|
№ |
Амалий машғулот мавзулари
|
Тингловчининг ўқув юкламаси, соат |
|||
|
Аудитория ўқув юкламаси жумладан |
|||||
|
Ҳаммаси |
Жами |
Амалий машғулот |
Мустақил таълим |
||
|
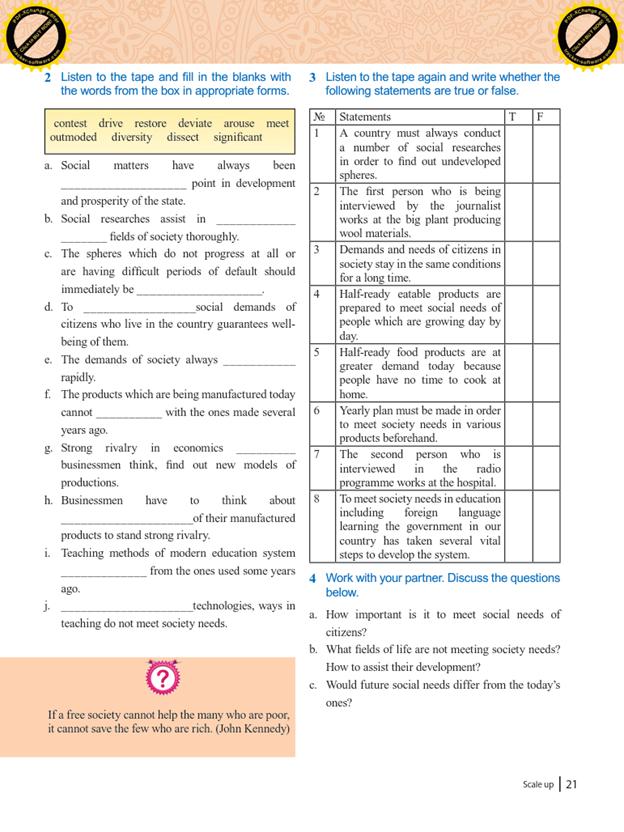
Unit 2. Lesson 4 Meeting society needs Starter: Eliciting s’s answers, p. 20 Listening: EX: 1-4. P. 20-21 Speaking: P 21. What fields of life are not meeting society needs? |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
2. |
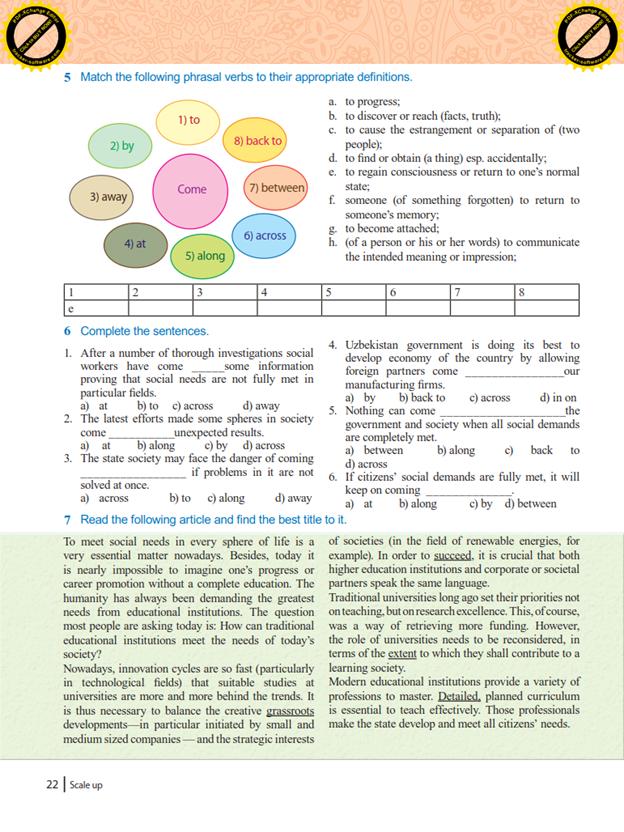
Unit 2. Lesson 5.Networking Starter:A Mindmap Listening: EX: 1-3. P. 24-25 Speaking:EX: 4. P. 25 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
3. |
Unit 2. Lesson 6. Professional contentment Starter:Working with pictures. Eliciting answers. Listening:EX: 1-4. P. 28-29 Speaking:EX: 5-6. P. 29-30 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
20 |
|
|
Жами |
|
6 |
6 |
60 |
ЎҚИТИШ ШАКЛЛАРИ
Мазкур фан бўйича қуйидаги ўқитиш шаклларидан фойдаланилади:
- амалий машғулотлар (маълумотлар ва технологияларни англаб олиш, ақлий қизиқишни ривожлантириш, олинган билимларни мустаҳкамлаш);
- давра суҳбатлари (кўрилаётган лойиҳа ечимлари бўйича таклиф бериш
қобилиятини ошириш, эшитиш, идрок қилиш ва мантиқий хулосалар чиқариш);
- баҳс ва мунозаралар (лойиҳалар ечими бўйича далиллар ва асосли аргументларни тақдим қилиш, эшитиш ва муаммолар ечимини топиш, танқидий фикрлаш қобилиятларини ривожлантириш).
БАҲОЛАШ МЕЗОНИ
II. МОДУЛНИ ЎҚИТИШДА ФОЙДАЛАНИЛАДИГАН ИНТEРФАОЛ ТАЪЛИМ МЕТОДЛАРИ
Ажурли арра методи
Ажур французча «ажоур» сўзидан олинган бўлиб, «бир ёқдан иккинчи ёққа ўтган,икки томони очиқ» деган маънони англатади.
Бу методдан фойдаланиш қуйидаги босқичларда амалга оширилади:
-тингловчилардан 4-5 кишилик кичик гуруҳлар ташкил этилади;
-тингловчиларга бериладиган топшириқ ва уларни бажаришда фойдаланиладиган матнли материаллар бир нечта асосий қисмлар (масалан, режа асосида бир нечта мавзучалар)га қирқилади;
-мавзучалар ва уларга доир матнли материаллар пакети кичик гуруҳларнинг ҳар бир аъзосига тарқатилади;
-кичик гуруҳ аъзолари матнли материаллардан фойдаланиб топшириқни бажаришга киришадилар;
-кичик гуруҳларнинг яхши ўзлаштирувчи аъзоларидан эксперт гуруҳи ташкил этилади;
-эксперт гуруҳи аъзолари қўлларидаги топшириқларни ҳамкорликда муҳокама қилишиб, бошқаларга ўргатиш режасини эгаллашадилар;
-экспертлар ўзларининг дастлабки кичик гуруҳларига қайтишиб ўрганганларини бошқа шерикларига ўргатишади.
Ўқитишга бундай ёндашилганда тингловчиларнинг ҳамкорликда ишлашларига ва катта ҳажмдаги ўқув материалларининг ўзлаштирилишига эришилади.
Бу методдан фойдаланувчи педагог тингловчиларга тақдим этилган топшириқни бажаришга доир материалларни қунт билан ўрганишни, биргаликда муҳокама этишни, савол-жавоб қилишни, ўрганганларини бошқаларга ўргатишлари зарурлигини олдиндан айтади.
Синектика методи
Бу метод амалий машғулотлар учун қулай бўлиб, «ақлий ҳужум» методига яқин. Бунда тингловчи дарсда қўйилган муаммони ҳал қилиш юзасидан аналогияга асосланган ҳолда ўз фикрларини, қарашларини олға суради. Бунда аналогия бевосита, шахсий, рамзий ва хаёлий бўлиши мумкин.
Думалоқ стол методи
Бу метод амалий машғулот учун қулай. Бунда ўқитувчи томонидан битта савол ёзилган варақ кичик гуруҳга тақдим этилади. Тингловчилар ўзларининг исми-шарифлари ва саволга жавобларини ёзиб, варақни ёнидаги тингловчига узатади. Шу тариқа ёзилган жавоблар йиғиштириб олиниб, тингловчилар иштирокида нотўғрилари ўчириб чиқилади ва натижалар баҳоланади.
Ручка стол устида методи
Бу метод амалий машғулот учун қулай. Саволга ўзининг жавоб вариантини ёзган кичик гуруҳдаги тингловчи ручкасини стол устига қўйиб варақни ёнидаги шеригига узатади. Саволга жавоб ёза олмаган тингловчи ручкасини столга қўймайди. Бир нечта кичик гуруҳлардаги тингловчиларнинг қўйилган бир хил саволга жавоблари йиғиштириб олиниб биргаликда муҳокама қилинади. Бу методнинг афзалликлари: ўқитувчи машғулотга ким тайёр, ким тайёр эмаслигини кўриб туради; машғулотга тайёрланмаган тингловчи оғзаки муҳокама пайтида кўриб чиқилаётган мавзу юзасидан анчагина фойдали билимлар олади; бу метод кичик гуруҳда олиб бориладиган иш бўлиб, тингловчи интизомини мустаҳкамлайди ва уларни жипслаштиради, чунки ўзининг жавоб вариантиустида узоқ ўйлаб ўтирадиган тингловчи бутун гуруҳга ажратилган вақтни сарфлаб юборади. Шунингдек тингловчи машғулотга тайёр бўлмаса, бунда ҳам гуруҳга панд беради; тингловчилар ўз жавобларини икки марта, яъни ёзма иш пайтида ва оғзаки муҳокама вақтида таҳлил қилиб чиқишади.
Ротация методи
Бу метод машғулот мавзуини ҳар бир кичик гуруҳ алоҳида-алоҳида муҳокама қилиб чиқиши, ёзганларини бутун гуруҳ жамоа бўлиб таҳлил қилиб кўриши учун қўлланилади ва қуйидаги босқичларда амалга ошири -лади:
-дарс мавзуси бўйича номерланган топшириқлар (масалан, режадаги мавзучалар) плакатларга ёзилиб доскага осиб қўйилади;
-топшириқлар сони учта бўлса, тингловчилар ҳам шунча кичик гуруҳ -ларга ажратилади ва гуруҳчалар номерланади;
-кичик гуруҳлар ўзларининг номерларига мос номердаги топшириқни ва уни бажаришда фойдаланиладиган ёзма маълумотлар пакетини олади;
-кичик гуруҳлар ўзларига тақдим этилган материалларни ҳамкорликда ўрганишиб топшириққа жавобларини ёзишади;
-жавоблар кичик гуруҳдаги ҳуснихати чиройли бир тингловчи томонидан ёзилади;
-топшириқларга ёзилган жавоблар варағи, маълумотлар пакети кичик гуруҳлараро алмаштирилади ва қўшимчалар қилинади, бироқ жавобларнинг такрорланишига йўл қўйилмайди;
-жавоблар қайси кичик гуруҳники эканлиги ажралиб туриши учун уларга ҳар хил рангдаги фламастерлардан фойдаланиш тавсия этилади. Шунингдек кичик гуруҳлар номерланиб, улар ўзларининг жавобларини шу номер остида ёзишлари ҳам мумкин;
-жавоблар ёзилган варақлар доскадаги осиғлиқ плакатларга скочда ёпиштирилиб, ўқитувчи иштирокида муҳокама қилинади, умумлаштирилади ва тўғри жавоблар дафтарларга ёзиб олинади;
-тўғри ва мукаммал жавоблар сонига қараб тингловчилар рағбатланти- рилади ва баҳоланади.
Галереяни айланиш методи
Кичик гуруҳларнинг барча аъзоларига битта муаммо таклиф этилади. Ҳар бир
кичик гуруҳ ўзларига берилган муаммога белгиланган вақт ичида фикрларини ёзиб, жавоблари ёзилган варақларини бошқа гуруҳ билан алмаштиради. Жавобларни олган гуруҳ уларни баҳолайди ва тугал бўлмаса ўз вариантлари билан тўлдиради. Сўнгра гуруҳлар фикрлари умумлаштирилиб, энг юқори баллга арзийдиган тўғри ва мукаммал жавоблар танлаб олинади.
Қор бўрон методи
Иккига ажратилган гуруҳ тингловчилари бир муаммо юзасидан энг кўп тўғри жавоблар топиш мақсадида биргаликда муҳокама юритишади. Ҳар бир тўғри жавоб юмалоқланган қор кўринишида ўша гуруҳ ҳисобига ёзиб қўйилади; тўпланган умумий баллар миқдори асосида гуруҳлар баҳоланади.
Асалари галаси методи
Муаммо битта гуруҳда ёки икки кичик гуруҳларда муҳокама қилинади. Бунда топшириқлар ҳар хил ёки бутун гуруҳга битта бўлиши мумкин. Гуруҳлар қўйилган муаммони маълум муддат муҳокама этиб, натижани бошқаларга маълум қилишади. Муаммо ечимининг энг яхши варианти танлаб олинади.
Думаловчи қор уюми методи
Думаловчи қор уюми методи ўқув машғулоти ўтказиш методининг рамзий номи бўлиб, иш қўйилган муаммо устида мулоҳаза юритиб кўриш учун тингловчиларга вақт, тегишли манбалар, тарқатма материаллар беришдан бошланади. Бу метод гуруҳнинг ҳар бир аъзосига бутун гуруҳнинг билимлари ва тажрибаларидан фойдаланиб, ўзининг кенг қамровли нуқтаи назарини баён этишни назарда тутади. Бунинг учун тингловчилар 4 та кичик гуруҳларга ажратилади. Муҳокама қилиб чиқиш учун барча гуруҳларга битта топшириқ берилади. Ҳар бир кичик гуруҳ топшириқ устида алоҳида ишлайди. Сўнгра биринчи билан иккинчи ва учинчи билан тўртинчи гуруҳлар муаммо устида биргаликда муҳокама юритишади. Охир оқибатда барча кичик гуруҳлар бирлашиб, бутун яхлит гуруҳ бўлиб қўйилган муаммо ечимини ҳал этишнинг турли йўлларини, вариантларини муҳокама қилишади. Бундай муҳокама жараёнида тингловчиларнинг қўйилган муаммо юзасидан билимлари чуқурлашиб, ойдинлашиб, бойиб, кенгқамровли бўлиб боради.
Синдикат методи
Гуруҳ учта кичик гуруҳларга бўлинади. Бунда таклиф этилаётган топшириқ уч хил нуқтаи назардан ҳал этилиш зарур. Масалан, уч ноъмалумли учта тенгламалар системасини ечиш топшириғи берилган бўлсин, у ҳолда биринчи гуруҳ масалани Гаусс, иккинчи гуруҳ Крамер, учинчи гуруҳ матрица усулидан фойдаланиб ечади. Сўнгра ечимлар биргаликда муҳокама этилиб, умумлаштирилади.
Аквариум методи
Гуруҳдан уч тингловчи ажратиб олиниб уларга хона ўртасидаги стол атрофига ўтиришлари ва қўйилган муаммони ўн минут атрофида биргаликда муҳокама, қилишиб фикр билдиришлари сўралади. Бу уч тингловчи аквариумдаги балиқларга қиёс. Атрофда ўтирган кузатувчилар ўртадаги тингловчиларнинг фикрларини диққат билан тинглаб, жавобларни тўғри ва нотўғрига ажратиб ёзиб боришади ҳамда муҳокама пайтида ўзларининг қарашларини баён этишади. Етарли даражада фикр билдира олмаган ўртадаги тингловчилар ўз ўринларини кучли фикр билдирган кузатувчи тингловчиларга бўшатиб беришади. Ҳар бир муаммо юзасидан билдирилган фикрлар тингловчилар иштирокида ўқитувчи томонидан умумлаштирилади.
Рақамли методлар
Гуруҳдаги тингловчиларнинг умумий сонидан келиб чиққан ҳолда 4х4х4, 5х5х5 ёки 6х6х6 методларининг биридан фойдаланилади. Масалан, 5х5х5 методида ҳар бири 5 тингловчидан иборат 5 та кичик гуруҳчалар ташкил этилиб, уларнинг 5 нафар сардорлари тўпланишиб қўйилган муаммони ҳамкорликда муҳокама этишади, сўнгра ўзларининг гуруҳларига қайтишиб шерикларига масаланинг ечимини ўргатишади.
III. АМАЛИЙ МАШҒУЛОТ УЧУН МАТЕРИАЛЛАР
1 –мавзу. An introductory lesson. PERSONAL AND PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT.
Introductions. Directions: You and your classmates are going to interview each other and then introduce each other to the rest of the class.
Pair up with another student in the class. Interview each other. Then introduce each other to the rest of the class. In your conversation, find out your classmate's:
Name length of time in this city
Native country or hometown reason for being here
Residence free-time activities or hobbies
Take notes during the interview.
QUESTIONS:
1. What is your name?
2. Where are you from?
3. Where are you living?
4. Why are you here (in this class)?
5. Are you a student? If so, what are you studying?
6. Do you work? If so, what is your job?
7 . Do you have another reason for being here?
8. What do you like to do in your free time?
9. What is your favorite season of the year? Why?
10. What are your three favorite books? Why do you like them?
11. Describe your first day in this class.
12. What is your favorite film? Why do you like it?
13. What is your favorite subject? Why do you like it?
14. Describe your study at the university.
1. Look at the pictures and share your ideas with your partner.
1. Is it easy to develop professionally alone or do you need peer or group support? 2. What activities lead to personal achievement?
3. Do you prefer to stay at the same point for many years or change it time by time?
1.Match the words 1-10 with their definition a-j.
|
1. |
aid (v) |
A) |
rationally |
|
2. |
advice (n) |
B) |
the feeling of being certain that something exists or is true |
|
3. |
efficiently (adv) |
C) |
money which is owed to someone else |
|
4. |
recover(v) |
D) |
unequal |
|
5. |
belief (n) |
E) |
clearly shown |
|
6. |
debt (n) |
F) |
an opinion which someone offers you |
|
7. |
affect (v) |
G) |
to harm or spoil something |
|
8. |
damage (v) |
H) |
to get back something lost |
|
9. |
unique (n) |
I) |
help or support |
|
10. |
define (v) |
J) |
influence |
2. Listen and decide if the statements are true(T) or false (F).
|
№
|
Statements |
T |
F |
|
1. |
It is crucial to research different sources of information to support your goals in personal development |
|
|
|
2. |
|
|
|
|
3. |
Use your working time rationally so you are able to do more in a shorter amount of time. |
|
|
|
4. |
Health is not connected with the personal development so there is no use |
|
|
|
5. |
Almost all people have the same skills, which make the people similar to each other on the planet we live on. |
|
|
|
6. |
If you are getting angry, think ten seconds before saying something. |
|
|
3. Fill in the gaps with words in ex.1.
1. It is important to research various sources of information to _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ with your goals in personal development.
2. Taking more breaks actually gives your mind a chance to _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _, allowing you to return and work more_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _.
3. You must know your _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ are in order to make a self- improvement plan. It wouldn’t make sense to work on areas of your life.
4. Stress can_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ your body, so take it all in single step.
5. Make a target goal for yourself. Goals that are specifically_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ will have specific results.
4. Read the text and give a title to it.
One way we plan for the future is by setting goals. A goal is the end toward which effort is directed. Goal setting is a major component of the career planning process. Your goals, and the steps you take to achieve them, will make up your career action plan. This is the road map that will take you from choosing a career to succeeding in it. In this context, your goals will be your career objectives, for example a particular occupation, a step on the career stairs or an earnings level.
Short-term goals and long-term goals. Goals can be widely classified into two categories: short-term goals and long-term goals. Generally, short-term goals are those you can achieve in six months to three years while it can take three to five years to reach long term ones. Your long term goals may be, for instance, earning a bachelor’s degree in accounting, passing your certified public accounting exam and getting a job as an accountant. Your short-term goals, which will lead to achieving your long term ones, might be completing your college applications, getting accepted into college, enrolling, and earning a good grade point average.
How to increase chances for success. It’s fairly simple to state a goal but actually achieving it isn’t quite as easy. Of course your actions are the biggest factor in deciding whether or not you will succeed but how you formulate your goals is almost as important. Make sure they meet these criteria:
Your goals must be specific. One might say, «I want to be successful.» Well, who doesn’t? But can you explain what success means to you? Success to one person may mean becoming manager of a company while to another person it can mean getting home from work by 6 o’clock every night.
You must be able to measure the outcome of your goals. When you set a goal you must include a time frame for achieving it. You can also specify amounts.
For example one can say «in three years I want to be halfway through graduate school.»
Don’t be negative. Make sure your goal is something you want rather than something you want to avoid. For instance instead of saying «I don’t want to stay in this job for another four years,» say «I want to improve my skills over the next four years so that I qualify for a better job.»
Keep your goals realistic. Make sure your abilities and skills are compatible with your long-term goals. Your goal shouldn’t be «I want to win a Grammy Award next year» if you don’t have a recording contract, haven’t made a record and can’t even carry a tune.
Can you reach a goal within your time frame? Don’t set yourself up to fail. If you have one big goal then you have to break it down into smaller parts, or short term goals. Remember, you will do better if you take baby steps than one big giant movement.
There must be an action tied to each goal. For instance if your goal is to graduate from college three years from now, the action tied to it would be to complete the remaining credits you need to complete your bachelor’s degree.
Be flexible about your goals. If you meet barriers that seem like they might slow down your progress, don’t give up. Instead, change your goals accordingly. Let’s say you have to work and can’t complete a bachelor’s degree in four years. You can enroll in school part-time and change your time frame. However, if a particular goal becomes something that is no longer important to you, then you should consider letting it go. That will allow you to put your energy into trying to get objectives that are important to you. Setting goals will not guarantee you a successful future. It will increase your chances greatly and that is the best thing you can ask for.
5. Give definitions to the highlighted words and find synonyms to them.
1. effort- physical or mental activity needed to achieve something, attempt
2. formulate ________________________________ ______________________
3. outcome _________________________________ ______________________
4. qualify __________________________ ______________________________
5. compatible _______________________ _______________________________
6. enroll ___________________________________ ________________________
6. Fill in the gaps using the words from the box.
break down, major, guarantee, fairly
1. Goal setting is a _____________________ component of the career planning process.
2. It’s ______________ simple to state a goal but actually achieving it isn’t quite as easy.
3. If you have one big goal then you have to _ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _it into smaller parts.
4. Setting goals will not _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ you a successful future.
7. Talk with your partner about personal and professional development. Use tips mentioned in the listening and reading tasks.
Which suggestions and tips are applicable for you? Share and discuss your ideas.
8. Think and write your future plans.
Set some goals and objectives to achieve them. Prioritize your objectives.
Include:
— which tips will be helpful for you according to the listening and reading passages?
— do you use them in your own personal and professional development? Why?
Writing: Write your future plan.
2 –мавзу. UBIQUITY OF ENGLISH
1. Look at the pictures and answer the following questions.

1. What words come to your mind when you see pictures?
2. What language are these words and do they have any equivalents in your own language?
3. What other examples of English in your daily life can you give?
2. Look through the following questions. Listen and according to the record choose the right answers. (More than one answer is possible).
1. What makes communication easier?
a) language learning b) words c) Knowledge of English
2. What languages were offered as an alternative international language?
a) Chinese, Russian b) Mandarin, French c) Esperanto
3. In what areas of Tashkent city English signs are less popular?
a) Chorsu, Chupon ota, b) Kukcha c) all areas
4. What does she think is a good place to enlarge one’s vocabulary?
a) City center b) Chupon ota street c) language centers.
3. Complete the sentences using the expressions from the box. Explain their meaning.
is inevitable; tonal nature; constructed rationally; in the foreseeable future;
to say nothing of; inveterate homemakers;
1. In order to make it neutral and easily absorbed Esperanto was _____________
2. It ______________ that English becomes a single international language.
3. A specific ______________ of Chinese language hampers its spreading.
4. Popularity of French as a language of diplomacy and exchange is ___________
5. English is unlikely to be replaced by any other language ___________________
6. Common word and expressions like ‘open’, ‘close’, ‘enter’, ‘shop’, ‘happy’ are popular even among _________________________
7. English words are frequent enough in all cities and towns ________________ touristic centers.
4. Read the text. Match the definitions 1-6 to the highlighted words and expressions in the text.
1. the medium, method, or instrument used to obtain a result or achieve an end ____________________
2. to come or bring into being __________________
3. very steep ________________________________
4. before, until ______________________________
5. time in the past when something or someone was popular or common________
6. easy to see or understand; evident___________________
5. Read the text: WORKING LANGUAGE
A lingua franca (LF) is a working language used by different populations to communicate when they do not share a common language. It is also called a bridge language, vehicular language or unifying language. Generally, a lingua franca is a third language that is distinct from the native language of both parties involved in the communication, sometimes for commercial reasons («trade languages»), but also for diplomatic and administrative convenience, and as a means of exchanging information between scientists and other scholars of different nationalities. The use of LF may be almost as old as language itself. Certainly, they have existed since antiquity. The term originates with one such language, Mediterranean LF. Latin and Greek were the LF of the Roman Empire.
Arabic was another early LF to develop because of the sheer size of the Islamic Empire dating back to the 7th Century. Arabic also served as the LF of science and diplomacy in the 1200’s because at that time, more books were written in Arabic
than in any other language. Still in some European languages (including Georgian), there are some Arabic words as admiral, algorithm or aubergine. Malay was the LF of Southeast Asia and was used by Arab and Chinese traders there prior to the arrival of the Europeans. Once they arrived, people like the Dutch and British also used Malay to communicate with the native peoples.
In fact, in it’s time distinct spheres used to have distinct LF, for example, Latin – in science. In 1687, Isaac Newton published his “Mathematic Principals Of Natural Philosophy” in Latin. English interpretation was published only 42 years later after his death. Today, LFs play an important role in global communication as well. Examples of LFs remain numerous, and exist on every continent. The most obvious example as of the early 21st century is English. The United Nations defines its official languages as Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and Spanish. The official language of international air traffic control is English. In certain countries, the LF is also used as the national language; e.g., Urdu is the LF of Pakistan as well as the national language.
6. Which of the following bits of information is not given (NG) in the text?
1. Lingua Franca is a single language for traders from all around the world. ___
2. A greater amount of books in XIII century were written in Arabic language. ___
3. Before Malay, people used Arabic in Southern Asia. ___
4. Isaac Newton’s book was published after his death. ___
5. Still, there are some lingua francas in different places. ___
6. Nowadays, all the pilots communicate in their own lingua franca. ___
3 –мавзу. INFORMATION AND SECURITY
1. Look at the picture and answer the questions below.

• What is the message of the picture?
• What do you think is connection between people and information?
2. Match the following treats with the adequate threats.
Threats Treats
• Hacking • Immune tolerance
• Ideological pressure • Law on Intellectual Property
• Infringe copyright • Updating Software
3. Listen to the survey interview. Decide which University students have been interviewed and list them down.
a. _________________________________________
b. _________________________________________
c. _________________________________________
d. _________________________________________
4. Write the names of students with the questions they have answered.
1. How do you understand IT attacks? __________________________________
2. How can we get protected from IT attacks? ____________________________
3. How do you understand Intellectual Property? ________________________
4. How can we protect Intellectual Properties? ____________________________
5. How do you understand Ideological Pressure?__________________________
6. How can we protect our youth from Ideological Pressures?________________
5. Work in pairs. Read the statement and discuss it.
Ideological attack is more powerful than military assault.
6. Read the text, choose and circle the appropriate heading for each paragraph.
Headings:
1. Dangers of Virtual World / Stealing Information / Hacking
2. Information for Business / Infringement of Copyright is Illegal / Intellectual Property
3. Ideological Pressure / Ideology is Bad / Ideology is a Set of Ideas
4. Information is Speeding / Difference between Attacks / Introduction
a. As there are advantages and disadvantages of every invention, sphere, and revolution, speeding of information also has two sides. When something
happens or is discovered or invented in one corner of our planet, the whole world learns about it immediately. But there is a notion of information attack. It can be understood in two ways; the first interpretation is “attack to information” and the
second is “attack somebody or something with the help of information”. Both of them are more dangerous showing catastrophic consequences than any type of attack with weapons or tanks.
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
b. Attack to information is penetrating into ones PC and monitoring, snooping, spying, stealing information and so on. The worst site is that is easy to hack (steal) your information virtually and even you do not know when, how and who hacked
and usually you cannot mind the event or object to. But Spying is sometimes legal, because you click on “I accept” in the licence agreements written in small prints even not reading.
c. Information threat in business purposes also exists; it can be understood as attack to intellectual property. What is an intellectual property? Simply, we can say that it is someone else’s intellectual working results such as musical, literary, and artistic works; discoveries and inventions; and words, phrases, symbols (trademarks), and designs. But owners usually suffer from not being able to
prove that idea was originally created by them. File swapping with your friend is also against law.
d. Attack with the help of information is making someone or group of people accept someone’s ideas, set of beliefs or ideological views; especially it is made with pressure in different ways. Those ways may be encouraging, persuading or even financially supporting.
7. Look at the following chart and answer the question.
What is the chart about/what does it show?____________________
8. Choose one of the alternatives for the title.
a.
Statistics of data loss 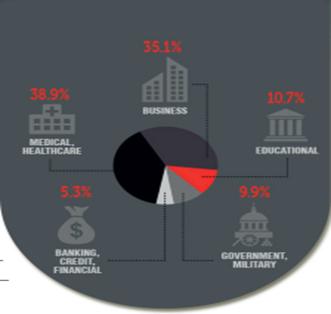
b. Rate of data loss
c. Data breach rates
9. Answer the questions.
1. What type of diagram is it?
_______________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
2. Which industry suffers most?
_____________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
3. Which sphere is recorded with the least rate of data breach?
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
4. Which industry is represented as in the second place by lose?
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
5. Why do you think government/military sphere has a little breach?
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
10. Write a description of the chart using the given adverbs.

11. Draw a pie chart with imaginative percentage of internet users by age (the elderly aged, middle-aged, adults, teenagers, the young etc) in Uzbekistan. And write essay within 150 words.
.
4- мавзу. STUDYING WITH MULTIPLE SOURCES
1. Look at the people in the photos and tell what they are doing and what they have in common.

Fill in the gaps using the words from the box.
contend stumble undoubtedly commonalities
conception route
1. Additional readings and alternative sources undoubtedly create a richer understanding.
2. Scientists ____________ that working with primary source is more effective then with secondary source.
3. When working with single source you may ___________________ upon unclear information.
4. Learners should discern the ________________ between materials.
5. When surfing through different sources relating materials to the objective helps to form a clear _______________________________ of idea.
6. Secondary source materials are more indirect _______________ to the same information than primary source._______________________________ of idea.
Read the statements. Listen to the conversation and put the statements in order they appear.
1 recent researches assert that learning with multiple sources is more effective than with single one.
• ___ getting information in less structured text is comparatively more challenging than in well structured texts.
• ___ strategies of working with multiple sources should be taught.
• ___ it’s better to understand connection than to learn detail by heart.
• ___ one should be able to filter the context.
Read the recommendations. Listen to the conversation again and tick (√ ) the information mentioned.
1. Consider the impact of, and evaluate conflicts.___
2. Try to use primary source. ___
3. Analyze commonalities. ___
4. Use in-class or on-line discussion time. ___
5. Engage sources with facts. ___
6. Refer to secondary source if primary one is not available. ___
7. Practice and familiarize materials. ___
8. Practice with multiple texts to improve your evaluative skills. ___
Read the sentences below and decide whom they belong to according to the script.
a. Seeing emotions and hearing their tone will surely improve the comprehension.
b. Multiple sources demand great analytical procedure.
c. Refer to shorter, more focused sources.

Work in pairs. Discuss the following questions. Provide specific example.
— What are the primary and secondary sources in your studies?
— What are the effects of those sources?
Comparisions as….as, not so/as….as.
Make up sentences using comparatives given below.
Eg.: Studying with single source is not as effective
as studying with multiple ones.
a. ___ not as important as…
b. ___ as comfortable as…
c. ___ not nearly as useful as….
d. ___ as interesting as….
e. ___ ot quiet as difficult as
f. ___ as usefull as…
g. ___ just as good as…
h. ___ as much as possible….
Find which words in A column go with the one in B to form common coparative expressions with as ….as and make up sentences of your own:
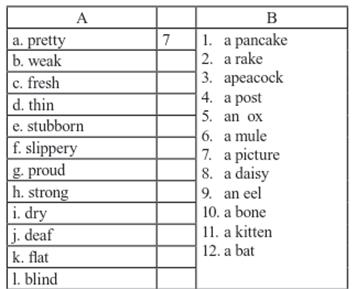
Complete the sentences with the expressions in Ex. 7.
Eg: - The girl entering the library looks very nice, doesn’t she? -Oh yes, she is as pretty as a picture.
1. Ali is _________________________ he can’t see anything without his glasses.
2. Oh, dear! We will have to change a tyre, it is ______________________.
3. If it doesn’t rain soon, they will never grow anything in their garden, it is _______________________.
4. Shoyad had a good sleep last night, so he is _________________________ in the morning.
5. Salim’s friends woudn’t lend him any money, he is ________________.
6. Nabi has been in bed all week with a cold and he was ____________________.
7. My sister’s daughter has been offered a place at the university. She is ________________. She has already told all her relations.
8. Davron has lost a lot of weight. Do you think he is OK? He looks ___________ to me.
9. Olim is _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ Once he makes up his mind he does it. Nothing can stop him.
Read the text and circle the best title from the box.
1. Studying with multiple sources 2. Getting information from different
sources 3. Benefits of using multiple sources 4. Giving references
Multiple sour-ces comprises the following: lectures, textbooks, fictional story novels, interviews and biographies, duplicates handouts, originals source materials, electronic media, Internet and others. Stahl, et al (1998) found that using multiple text-sources can only be effective if we are taught to use them properly. Studying with multiple sources offers a fundamentally different view of the learning process from the traditional studying based on the use of single sources to complicated, up-
to-date ways of the study i.e. studying with multiple sources, where new knowledge is achieved through confrontation among different sources. Furthermore, it is not only getting additional information and perspectives from different sources, but also implementing acquired knowledge in actions
in real life.As Kolb, D.A. (“Experiential learning: experience as the source of learning and development”, Oxford University press, 2010, p.138) points out: “…studying is a skill, being successful in life requires many different skills, such as time-management, self-discipline, concentration, memorization, organization,
and effort. We must understand the nature and forms of human knowledge and the processes whereby this knowledge is created. It has already been emphasized
that this process of creation occurs at all levels of sophistication when studying with multiple sources”.
Studying with multiple sources has number of advantages and disadvantages:
To begin with advantages, it teaches learners to be effective and find proper use of the received material, which encourages students to be creative, selective and
develop their analytical skills and the most important thing is adapting acquired knowledge, where needed and using it in real life.
Secondly, information from different sources arouses students’ curiosity and increases their comprehension of additional materials and assists interacting or
engaging with facts, circumstances of the material, practicing and familiarizing with new material and concepts, improve their evaluative skills, like comparing,
contrasting and analyzing which is a great experience and big step forward
towards a future career.
Thirdly, it helps learners to impede their learning by analyzing, reorganizing or synthesizing and filtering information as these skills impact the development of
a person.On a level with advantages studying with multiple sources has a number of disadvantages like challenges in understanding of the received material because
of their academic nature and tremendous size while processing, time consumptions owing to the variety of sources, concealment of bias and others.( Studying
with multiple sources. Study guides and strategies. http://www.studygs.net/ multiplesrc.html) Finally, in addition to these practical benefits studying with multiple sources provides wide range of opportunities in being more self-confident and enterprising. Furthermore, multiple sources can greatly improve and dress experience of learners if they know to use them properly.
Answer the following questions.
a. Which sources of study have been mentioned in the text?
b. Are you more inclined to use traditional primary sources or up-to-date ways of studying? Why?
c. To what extent do you think studying with multiple sources is better than using single source?
d. To what extent did the author use references in the text?
2 семестр. 1 мавзу.




2 мавзу




3 мавзу.


4 мавзу.





3 семестр .1 мавзу.



2 мавзу.




3 мавзу.

4 мавзу.



4 семестр. 1 мавзу.




2 мавзу.


3
мавзу. 



4 мавзу.

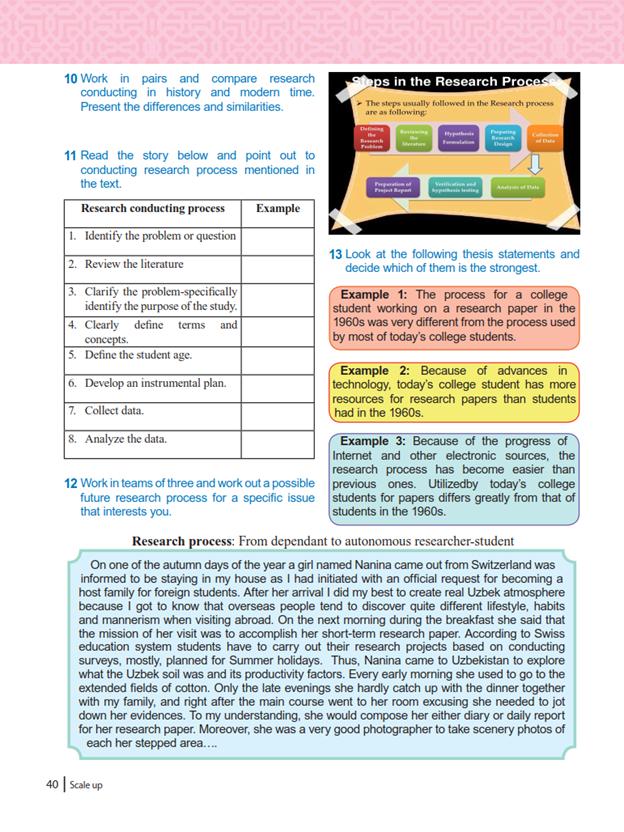

5 семестр. 1 мавзу

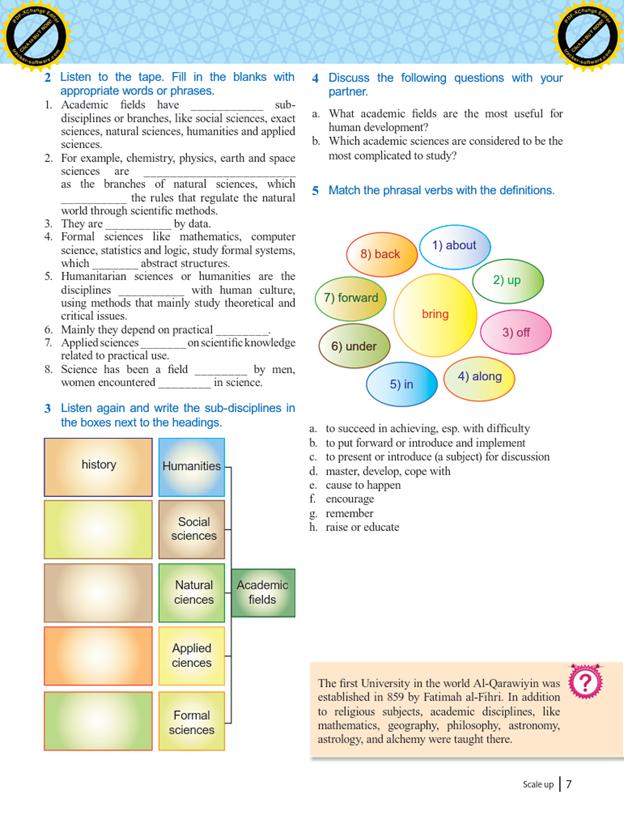



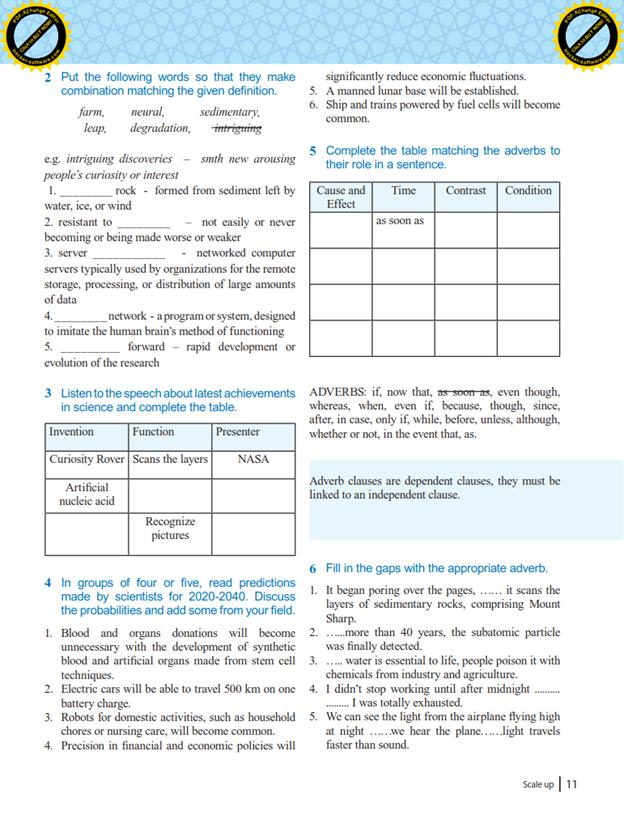


3 мавзу.

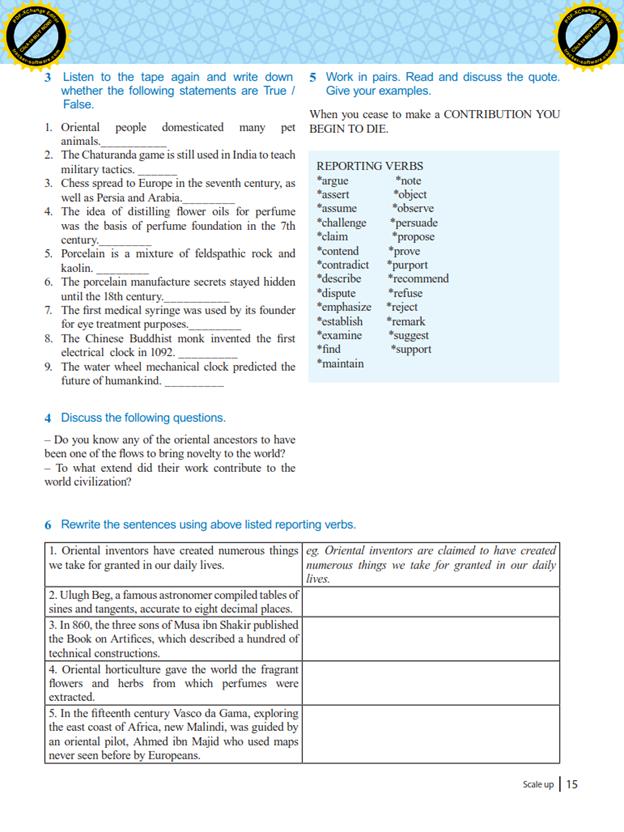
6 семестр.


2 мавзу.




3 мавзу .




ГЛОССАРИЙ
abbreviated-shortened; cut short
accessories-something added to a machine or to clothing, which has a useful or decorative purpose
accomplish-to finish something successfully or to achieve something
accurate-1) (especially of information, measurements, or predictions) correct in all details; exact accurate information about the illness is essential an accurate assessment (of an instrument or method) capable of giving accurate information
acoustic -if you refer to the acoustics or the acoustic of a space, you are referring to the structural features which determine how well you can hear music or speech in it.
acoustic-1.adjectiverelating to sound or hearing 2. describes a musical instrument that is not made louder by electrical equipment .
actual- real; existing in fact
adjust-to change something slightly, especially to make it more correct, effective, or suitable
Aerial [Radio]-noun[C]: A structure made of metal rods or wires which receives or sends out radio or television signals.
aerial-a structure made of metal rods or wires which receives or sends out radio or television signals
aid - 1. [ U ] help or support 2. [ C ] a piece of equipment that helps you to do something.
aircraft -any vehicle, with or without an engine, which can fly, such as a plane or helicopter .
alternate -one of two equal angles on opposite sides of a line that crosses two usually parallel (= always the same distance apart) lines, and on opposite sides of those lines .
amount -a collection or mass especially of something which cannot be counted
amplifier -noun [ C ] an electrical device which makes sounds loud.
amplifier-an electrical device which makes sounds louder
amplitude- 1)formal a large amount or wide range.2) [ C usually singular ]specialized the distance between the top and the base of a curve
angle-the space between two lines or surfaces at the point at which they touch each other, measured in degrees.
antenna - either of a pair of long thin organs which are found on the heads of insects and crustaceans (= animals with hard outer shells) and which are used to feel with
antenna - either of a pair of long thin organs which are found on the heads of insects and crustaceans (= animals with hard outer shells) and which are used to feel with .
application -[ C ] a computer program that is designed for a particular purpose.
artifacts-an object that is made by a person, such as a tool or a decoration, especially one that is of historical interest
associate-to connect someone or something in your mind with someone or something else
attenuate-to make something smaller, thinner or weaker
attics-noun a space or room inside or partly inside the roof of a building Origin: late 17th cent. (as an architectural term designating a small order (column and entablature) above a taller one): from French attique, from Latin Atticus 'relating to Athens or Attica'
audio amplifier- an electrical device which makes sounds louder
band[Group]-noun[C]: a group of people who share the same interests or beliefs,or who have joined together for a special purpose.
beacon -a light or fire on the top of a hill that acts as a warning or signal
benefit-a helpful or good effect, or something intended to help
benefit-a helpful or good effect, or something intended to help
Broadcast-broadcasts, broadcasting (The form broadcast is used in the present tense and is the past tense and past participle of the verb.)
broadcast-to send out a programme on television or radio .
cable -a set of wires, covered by plastic, that carries electricity, telephone signals, etc.
camera-a device for taking photographs or making films or television programmes
capture -to take someone as a prisoner, or to take something into your possession, especially by force
cell - the smallest basic unit of a plant or animal.
channel- a way of communicating with people or getting something done
circuit -a regular pattern of visits or the places visited
circuits-a regular pattern of visits or the places visited
coil-a long thin piece of something that forms rings or curls
colloquialism -noun [ C ] an informal word or expression which is more suitable for use in speech than in writing.
combination-1) a joining or merging of different parts or qualities in which the component elements are individually distinct a magnificent combination of drama, dance, and music the combination of recession and falling property values proved fatal to the business community this colour combination is stunningly effective [mass noun] the process of combining different parts or qualities or the state of being combined
commercially available-an advertisement which is broadcast on television or radio
communications device – devices for the communication, modem
component -a part which combines with other parts to form something bigger .
conduction-the process by which heat or electricity goes through a substance to organize and perform a particular activity
conductive- having the property of conducting something (esp. heat or electricity) to induce currents in conductive coils of or relating to conduction
connections- when someone or something is related to someone or something else
Consist -1) (consist of) be composed or made up of the crew consists of five men (consist in) have as an essential feature his poetry consisted in the use of emotive language 2) (consist with) be consistent with the information perfectly consists with our friend's account
conventional- traditional and ordinary
conversion-when someone or something is converted from one thing to another
convert - 1. [ T ] in rugby, to score more points after a try by kicking the ball over the bar and between the posts .2.noun[ C ] someone who changes their beliefs, habits, or way of living
corresponding-related to or connected with something
corresponds-1) have a close similarity; match or agree almost exactly the carved heads described in the poem correspond to a drawing of Edgcote House communication is successful when the ideas in the minds of the speaker and hearer correspond
counterparts-a person or thing which has the same purpose as another one in a different place or organization
crane-a tall metal structure with a long horizontal part which is used for lifting and moving heavy objects
creating-to make something new, especially to invent something
current -a movement of water, air or electricity, in a particular direction.
decode-to discover the meaning of information given in a secret or complicated way
developed- advanced or powerful
development -when someone or something grows or changes and becomes more advanced
Digital television-describes information, music, an image, etc. that is recorded or broadcast using computer technology
digital-adj: 1. describes information,music,an image,etc.that is recorded or broadcast using computer tecnology. 2. showing information in the form of an electronic display.
distance-the amount of space between two places
distinction-a difference between two similar things
educational- p roviding education or relating to education
effective-successful or achieving the results that you want
efficient-working or operating quickly and effectively in an organized way
electricalsignals-. Microprocessors by themselves only react to patterns of electrical signals.
electronic device-an object or machine which has been invented for a particular purpose
electronic -using, based on or used in a system of operation which involves the control of electric current by various devices.
element- a part of something
elements-1) an essential or characteristic part of something abstract the death had all the elements of a great tabloid story there are four elements to the proposal a small but significant amount of a feeling or quality
enclosure-an area surrounded by a fence or wall
encoding-to change something into a system for sending messages secretly, or to represent complicated information in a simple or short way
energy-the power and ability to be physically and mentally active
entertainment-noun [mass noun] the action of providing or being provided with amusement or enjoyment everyone just sits in front of the television for entertainment [count noun] an event, performance, or activity designed to entertain others a theatrical entertainment the action of receiving a guest or guests and providing them with food and drink
equipment-the set of necessary tools, clothing, etc. for a particular purpose
exclusively- only
exhibit-to show something publicly
fiber -a thread or filament from which a vegetable tissue, mineral substance, or textile is formed
film-a series of moving pictures, usually shown in a cinema or on television and often telling a story
frames -the basic structure of a building, vehicle or piece of furniture that other parts are added onto
frequency [Waves]-noun 1.[u] The number of times that a wave,especially a sound or radio wave is produced within a particular period,especially one second. 2.[c] a particular number of radio waves produced in a second at which a radio signal is broadcast.
frequency-noun pl. frequencies 1) [mass noun] the rate at which something occurs over a particular period of time or in a given sample an increase in the frequency of accidents due to increased overtime
generate -to cause something to exist .
generator -a machine which produces something, especially electricity .
HDTV -High-definition television
height-the distance from the top to the bottom of something, or the quality of being tall
hydraulic-operated by or involving the pressure of water or some other liquid
image-[ C ] a picture in your mind or an idea of how someone or something is
induction -noun [ C or U ] when someone is formally introduced into a new job or organization, especially through a special ceremony
installed -to put a computer program onto a computer so that the computer can use it
institution-1) an organization founded for a religious, educational, professional, or social purpose an organization providing residential care for people with special needs
intercom -a device which people speak into when they want to communicate with, for example, someone who is inside a building or in a different room
interlaced -to join different parts together to make a whole, especially by crossing one thing over another or fitting one part into another
Interlacing- to join different parts together to make a whole, especiallyby crossing one thing over another or fitting one part into another
intermittent -not happening regularly or continuously; stopping and starting repeatedly or with periods in between
internal tuner-The tuner in a radio or television set is the part which you adjust to receive different radio or television signals, so that you can watch or listen to the program that you want.
knock -noun [ C ] when something hard hits a person or thing
laser - (a device which produces) a powerful narrow beam of light that can be used as a tool to cut metal, to perform medical operations, or to create patterns of light for entertainment
lens -a curved piece of glass, plastic or other transparent material used in cameras, glasses and scientific equipment, which makes objects seem closer, larger, smaller, etc
light intensity- luminous intensity
lightweight-weighing only a little or less than average
loop-the curved shape made when something long and thin, such as a piece of string, bends until one part of it nearly touches or crosses another part of it
Loudspeaker- a piece of electrical equipment that allows sounds or voices to beheard loudly at a distance
magnetic fields - an area around a magnet or something magnetic, in which its power to attract objects to itself can be felt
mast-noun[C]: A tall metal pole used to support an aerial for radio or television signals.
maximize- to make something as great in amount, size or importance as possible.
megaphone -noun [ C ] a cone-shaped device which makes your voice louder when you speak into it, so that people can hear you although they are not near to you .
method-a particular way of doing something
Microphone - an instrument for converting sound waves into electrical energy variations which may then be amplified, transmitted, or recorded.
microwave - an electric oven that uses waves of energy to cook or heat food quickly.
mid-range-average in quality, size, or cost.
modulate -to change the style, loudness, etc. of something such as your voice in order to achieve an effect or express an emotion
modulate-to change something, such as an action or a process, to make it more suitable for its situation
monitor-1) a device used for observing, checking, or keeping a continuous record of something
motion -noun [ C or U ] the act or process of moving, or a particular action or movement
mount [Fix]-verb[T]: To fix something on a wall,in a frame etc.,so that it can be viewed or used.
mounted-describes soldiers or police officers who ride horses while on duty
movingimages-pictures that moves
multiple [Many]- adj: very many of the same type,or of different types.
multiple-ery many of the same type, or of different types
navigation -the act of directing a ship, aircraft, etc. from one place to another, or the science of finding a way from one place to another.
nervous system- the main system of nerve control in a living thing, consisting of the brain and the main nerves connected to it
numerous-many. We have discussed these plans on numerous occasions.
obsolete-not in use any more, having been replaced by something newer and better or more fashionable
omnidirectional-Telecommunications receiving signals from or transmitting in all directions
operation- the way that parts of a machine or system work together, or the process of making parts of a machine or system work together
operator-someone whose job is to use and control a machine or vehicle
optic- 1. relating to the eye or vision a lens or other optical component in an
optical instrument-optical tool
originally-first of all
pedestals-a long thin column which supports a statue, or a tall structure like a column on which something rests
permanently - always and forever
piezoelectric -adjective producing electrical power by putting pressure on particular types of stone .
pneumatic -operated by air pressure
pressure -noun 1. [ U ] the force you produce when you press something 2. [ C or U ] the force that a liquid or gas produces when it presses against an area
production- noun [ U ] the process of making or growing goods to be sold
professional-related to work that needs special training or education
progressive-developing or happening gradually
proportional-adjective corresponding in size or amount to something else the punishment should be proportional to the crime (of a variable quantity) having a constant ratio to another quantity
provide-to give someone something that they need
provide-to give someone something that they need
public -adjective 1. describes a place where a lot of people are 2.adjective provided by the government from taxes to be available to everyone
pulldown -a list of instructions on a computer screen, which you cannot see until you choose to see it
radar -a system which uses radio waves to find the position of objects which cannot be seen .
radiate -to produce heat and/or light, or (of heat or light) to be produced .
rate-the speed at which something happens or changes, or the amount or number of times it happens or changes in a particular period
reception [Radio/Television]-noun[u]:The degree to which radio or television sounds and pictures are clear.
recognition - noun 1. [ S or U ] agreement that something is true or legal 2. [ S or U ] If you are given recognition, people show admiration and respect for your achievements
record -verb [ T ] to keep information for the future, by writing it down or storing it on a computer
reflective- describes a surface which sends back most of the light that shines on it and which therefore can be seen easily
reflect-to show, express or be a sign of something
reinforcement-the process of reinforcing something.
relationship-noun the way in which two or more people or things are connected, or the state of being connected the study will assess the relationship between unemployment and political attitudes the state of being connected by blood or marriage
replaced -to take the place of something, or to put something or someone in the place of something or someone else
require- to need or make necessary
resistance-a force which acts to stop the progress of something or make it slower
resolution-an official decision that is made after a group or organization have voted
reverse-to change the order or development of events, a process, or a situation to be the opposite of what it was
rooftop antenna- an antenna onthe outside surface of the roof of a building
rooftop-roof·top the outer surface of a building's roof - shout something from the rooftops
sensor- noun [ C ] a device which is used to record that something is present or that there are changes in something .
sensor-a device which is used to record that something is present or that there are changes in something
set up-the way in which things are organized or arranged
set-top antenna- an electronic device that makes it possible to watch digital broadcasts on ordinary televisions
signal- a series of electrical or radio waves which are sent to a radio or television in order to produce a sound, picture or message
signal-1) a gesture, action, or sound that is used to convey information or instructions, typically by prearrangement between the parties concerned the firing of the gun was the signal for a chain of beacons to be lit
signal-an action, movement or sound which gives information, a message, a warning or an order
slender -thin and delicate, often in a way that is attractive
Smoking is likely to damage your health permanently.
sound waves-Physics a wave of compression and rarefaction, by which sound is propagated in an elastic medium such as air
source-1) a place, person, or thing from which something originates or can be obtained mackerel is a good source of fish oil
spacecraft -a vehicle used for travel in space.
specific- relating to one thing and not others; particular
speech- noun 1. [ U ] the ability to talk, the activity of talking, or a piece of spoken language 2. [ U ] the way a person talks.
speed-up-an increase in the rate of change or growth
spread-to (cause to) cover, reach or have an effect on a wider or increasing area
stereo -a way of recording or playing sound so that it is separated into two signals and produces more natural sound
superior -better than average or better than other people or things of the same type
supplant-to replace
surface- the outer or top part or layer of something
Television-1) [mass noun] a system for converting visual images (with sound) into electrical signals, transmitting them by radio or other means, and displaying them electronically on a screen
Television-1) [mass noun] a system for converting visual images (with sound) into electrical signals, transmitting them by radio or other means, and displaying them electronically on a screen
technique-a way of doing an activity which needs skill
telecommunication -(functioning as singular) the science and technology of communications by telephony, radio, television, etc
teleprompters-trademark( US trademark TelePrompter) an electronic device which makes it possible for broadcasters to read text while looking directly at the television camera
telescope- to make or become shorter by reducing the length of the parts
television transmission-Transmission in the television
termed -to give something a name or to describe it with a particular expression
transducer -noun [ C ] any electronic device that changes one form of energy into another, such as a microphone , which changes sound waves into electrical signals .
Transmitter- a piece of equipment for broadcasting radio or television signals.
transmitter-a piece of equipment for broadcasting radio or television signals.
tripods-a support with three legs for a piece of equipment such as a camera
tube-a long hollow cylinder made from plastic, metal, rubber or glass, especially used for moving or containing liquids or gases. the tube mainly US the television
tweeter-a speaker a piece of equipment that sound comes out of that is designed for high sounds.
typically -adverb in a way that shows all the characteristics that you would expect from the stated person, thing or group
UHF-radio waves between 300 MHz and 3000 MHz
ultrasonic -adjective describes sound which is too high for people to hear .
variation -noun [ C ] something that is slightly different from the usual form or arrangement
versatile -able to change easily from one activity to another or able to be used for many different purposes
VHF-radio waves between 30 to 300 MHz
vibrations- continuous quick, slight shaking movement
video camera-a camera which records moving pictures and sound onto a video
video formats-formats of video
video recordings-the recorded and stored video materials
voltage-the force of an electric current, measured in volts high/low voltages
watt-the standard measure of electrical power
wave -to raise your hand and move it from side to side as a way of greeting someone, telling them to do something or adding emphasis to an expression.
wavelength- the distance between two waves of energy, or the length of the radio wave used by a particular radio station for broadcasting programmes
wavelength-1) usu with A wavelength is the distance between a part of a wave of energy such as light or sound and the next similar part.
waves- the pattern in which some types of energy, such as sound, light and heat, are spread or carried
widely used -far apart; with a wide space or interval between
width -1) [mass noun] the measurement or extent of something from side to side; the lesser of two or the least of three dimensions of a body the yard was about seven feet in width [count noun] a piece of something at its full extent from side to side
woofer-a speaker designed for low sounds
3. INFORMATSION-USLUBIY TA'MINOT
3.1. Asosiy adabiyotlar:
1. Prezident I.A.Karimov asarlari 1992- 2016yy.
2. Kadrlar tayyorlash milliy dasturi va Ta'lim to'g’risidagi qonun // Oliy Majlis IX sessiyasi.
- T.,1997.
3. G. Bakieva, F. Rashidova va boshqalar. Scale up. 1,2,3, courses. Set of manuals for non
philological higher educational establishments.Tashkent, 2016.
4. Курашвили Е.И., Михалкова Е.С. Английский язык. Учебник для студентов I и II
курсов, начинающих изучение языка в техническом вузе. –М.: Высшая школа, 1982.
5. Новицкая Т.М., Кучин Н.Д. Практическая грамматика английского языка. – М.:
Высшая школа, 1983.
6. Muhitdinova G.SH. Tehnika Oliy O'quv yurtlari uchun. Ingliz tili darsligi. - T.:
Uzbekiston, 1997.
7. Marten Sevionyr. Word-Wise. – Т., 1997.
8. Cristopher Morris P.J. World English. – 1997.
9. Dudkina G.A. va boshqalar. English for businessmen. – Т., 1993.
10. Абдалина Е.Н. Учебник английского языка для студентов неязыковых вузов.Т, 1996.
11. Headway (Elementary, Pre-intermediate, Intermediate, Upper intermadiate).
CambridgeUniversity Press 2011.
12. G. Bakieva, F. Rashidova va boshqalar. Scale up. 1,2,3, courses. Set of manuals for non philological higher educational establishments.Tashkent, 2015.
3.2. Elektron adabiyotlar:
1. Santiago Remacho Esteras. Infotech English for Computer Users (4th ed.)
CambridgeUniversity Press 2011
2. Mary Glasgow Magazines. An imprint of scholastic inc. Time saver speaking activities.
2. Betty Azar_Understanding and Using English Grammar.pdf
3. Macmillan - Topics - Communication - Pre-Intermediate.pdf
4. Games For Vоcabulary Practice CambridgeUniversity Press 2 003. www.cambridge.org. wwwcambridge'org/978O521006451
5. Full contact.
6. English for you.
3.3. Internet veb-saytlar
1. htpp:www.bearingpoint.uz.
2. htpp:wwwiqlib.ru.book.preview
3. htpp:window.edu.ru/window/library
4. htpp:www.izdat-bspu.narod.ru/books.10.htm
5. htpp:netstate.com.
6. htpp:www.rbtl.ru
7. htpp:book.vsem.ru